Unlock the secrets of Spain’s tax system! Discover essential tips for digital nomads navigating taxes while living your dream abroad.

Image courtesy of Ono Kosuki via Pexels
Table of Contents
- Understanding Digital Nomad Status
- Tax Residency in Spain
- Double Taxation Agreement (DTA)
- Income Sources and Tax Implications
- Social Security Contributions
- Practical Steps for Compliance
- Benefits and Deductions
- Conclusion
Exploring Spain as a digital nomad is an adventure filled with vibrant culture, breathtaking landscapes, and delectable cuisine. However, while you’re enjoying the sun-drenched cafés and historic streets, it’s crucial to stay informed about the tax implications of living and working in this beautiful country. Understanding the Spanish tax system is key to seamlessly blending your work and travel experience without any unwelcome surprises. Let’s dive into what you need to know about taxes in Spain as a digital nomad from the USA.
Understanding Digital Nomad Status
So, what exactly is a digital nomad? In short, a digital nomad is someone who leverages technology to work remotely while traveling the world. These individuals often take advantage of flexible jobs that allow them to set up their laptops in exotic locations, coffee shops, or on sunny beaches. The lifestyle has gained immense popularity and, as a result, many countries, including Spain, have begun to facilitate the influx of digital nomads with various visa options.
The rise of digital nomadism is supported by a growing number of companies embracing remote work. It’s estimated that millions of people now identify as digital nomads, contributing significantly to their host countries’ economies and cultures. If Spain is calling your name, you can explore visa opportunities, such as the Non-Lucrative Visa, which is ideal for those who can sustain themselves financially without working locally, or the newly introduced Digital Nomad Visa that allows you to work remotely for a non-Spanish company.
Tax Residency in Spain
Understanding tax residency is crucial for anyone considering a long-term stay in Spain. Generally, if you reside in Spain for more than 183 days within a calendar year, you will be deemed a tax resident. This means that Spain may require you to pay taxes on your worldwide income—yes, that includes income earned from clients or employers outside Spain.
Being classified as a tax resident also imposes certain obligations. It’s essential to keep track of your days spent in Spain, as they can influence your residency status and tax responsibilities. If you find yourself visiting Spain frequently or staying for extended periods, be mindful of your total time spent there to avoid unexpected tax liabilities.
Embrace the freedom of being a digital nomad while mastering the art of navigating taxes in Spain. Knowledge empowers your journey and transforms challenges into opportunities.
Double Taxation Agreement (DTA)
One significant relief for US citizens living in Spain is the Double Taxation Agreement (DTA) between the two countries. The primary aim of this treaty is to prevent you from being taxed twice on the same income. Essentially, the DTA allows you to avoid being taxed by both the US and Spain on your earnings, which is excellent news for digital nomads trying to make the most of their financial situation.
When leveraging the DTA, you’ll primarily use methods like the foreign tax credit or exclusion to avoid double taxation, meaning you can potentially offset any taxes you owe in Spain with your US tax obligations. Don’t forget you’ll still need to report your international income to the IRS, typically via Form 1040 and Form 2555 if you qualify for the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion. It’s advisable to familiarize yourself with these forms and consider consulting a tax professional to navigate the process smoothly.
Income Sources and Tax Implications
As a digital nomad, understanding what types of income are taxable in Spain is fundamental. Income sourced from freelance work, remote jobs, or any other work that generates revenue is typically subject to Spanish taxes. The good news is that Spain’s tax brackets are well-defined, meaning you’ll know what percentage of your income you’ll need to allocate for taxes based on your earnings.
When it comes to tax rates, they can vary depending on where you reside in Spain, but generally, income tax rates can range from 19% to 47% for individuals, based on your income level. Additionally, be prepared to declare any income received from investments or rental properties in your home country, as those may also incur taxes if you’re deemed a resident.
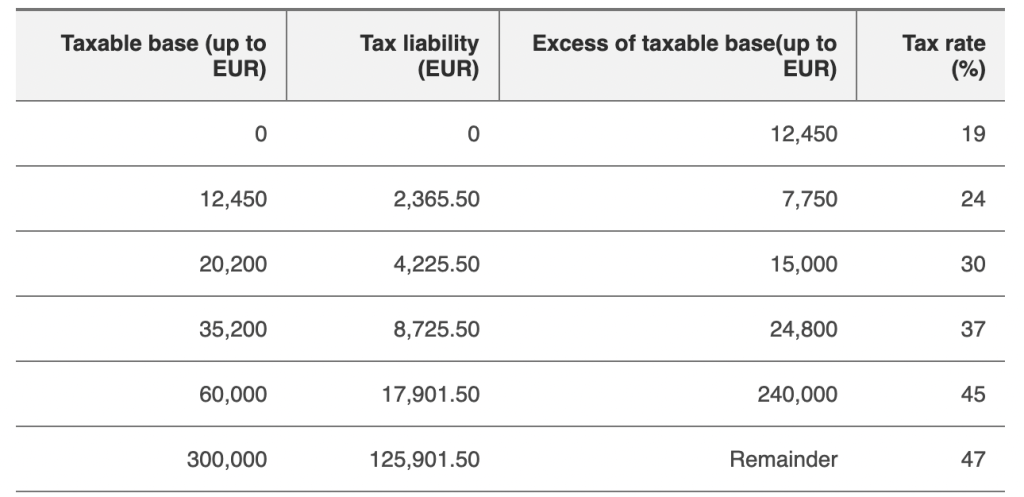
If you decide to work as a freelancer or start your own business while in Spain, you must register as a self-employed individual (autónomo). This entails filing quarterly tax returns and handling social security contributions. It may sound intimidating, but many resources are available to help guide you through the registration process.
Social Security Contributions
Social security may seem like a distant concern, but understanding its implications can be beneficial as a digital nomad in Spain. The United States and Spain have a bilateral agreement regarding social security, allowing you to avoid contributing to both countries’ social security systems simultaneously. If you’re working for a foreign employer while residing in Spain, you might be eligible for an exemption, but be sure to check the requirements.
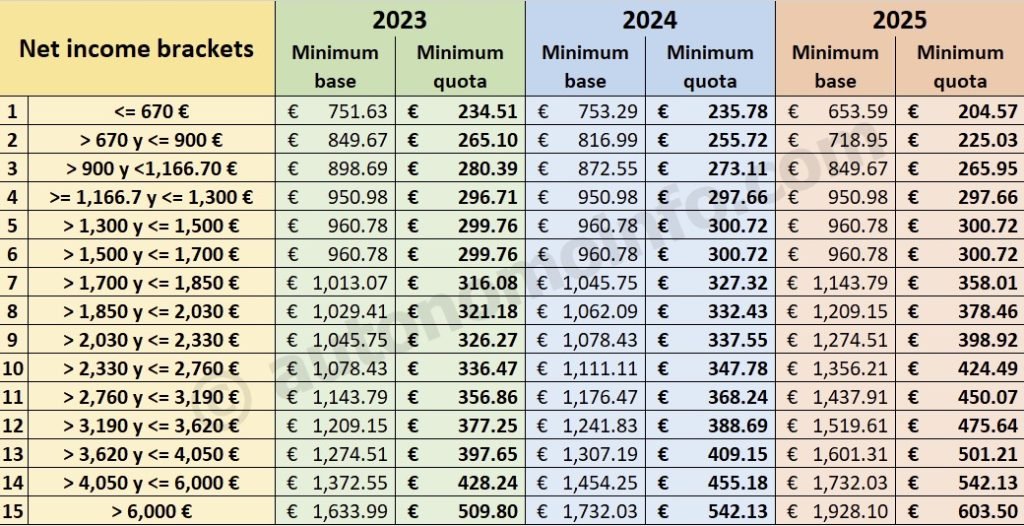
Contributing to Spain’s social security system may be mandatory if you start working with a local company or establish yourself as a freelancer. These contributions can have an impact on your benefits, including healthcare and pensions, so be sure to pay attention and understand your options.
Practical Steps for Compliance
Now that you’re aware of how taxation works, jumping into action is the next step. First, you’ll need to register with the Spanish tax authority (Agencia Española de Administración Tributaria or AEAT). This typically involves filling out necessary forms and providing documentation proving your residency status. Don’t be surprised if the registration process includes a few twists and turns, but at CarWay Migrate we can provide helpful guidance.
Remember to mark your calendar for tax filing deadlines! Spanish tax returns are usually due in June for the previous fiscal year, so plan ahead to comply with local laws. As a digital nomad, keeping organized records of your income and expenses related to your work will also make your tax filing experience smoother.
Benefits and Deductions
As a digital nomad, you’ll be pleased to know that Spain offers potential tax benefits and deductions. Depending on your income profile, you may qualify for deductions on social security contributions or work-related expenses. Keep track of all business-related expenditures for consideration when filing taxes; every little bit can add up!
Consulting with a tax professional can be a game-changer. Not only will they be familiar with international tax laws, but they can guide you towards maximizing your deductions and ensuring compliance with both Spanish and US tax regulations. Many expats in Spain find value in teaming up with a tax advisor who understands the intricacies of living and working abroad, so consider this option carefully. Fell free to book a call with us.
Conclusion
Navigating the tax landscape as a digital nomad in Spain may seem overwhelming at first, but understanding your obligations and rights can make it manageable. By familiarizing yourself with residency rules, tax treaties, and your tax responsibilities, you’ll not only stay compliant but also set yourself up for a worry-free experience living and working in this beautiful country. So pack your bags, grab your laptop, and get ready to enjoy the wonders of Spain while confidently managing your tax obligations.
Feel free to share your experiences or ask questions in the comments! We’re all in this together, and every story helps create a richer community for digital nomads.




